Cation
Tracer Diffusion in the Thermoelectric Materials Cu3Mo6Se8
and “β-Zn4Sb3”
Eric Chalfin, Hongxia Lu and Rüdiger
Dieckmann
Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Cornell University, Bard Hall, Ithaca, NY 14853-1501, U.S.A.
Abstract
The diffusion of radioactive tracers, Ag-110m
diffusing in Cu3Mo6Se8 and Zn-65 diffusing in
“β-Zn4Sb3”, was experimentally studied. Tracer
concentration profiles were generated by diffusion-annealing samples in argon
atmospheres containing 1-2 % H2. The corresponding residual
radioactivity profiles were measured and analyzed to determine tracer diffusion
coefficients of Ag-110m diffusing in Cu3Mo6Se8and
of Zn-65 diffusing in “β-Zn4Sb3”. The temperatures
investigated were between about 195 and 900 °C for Cu3Mo6Se8and
between about 195 and 475 °C for “β-Zn4Sb3”. It was found
that the diffusion of Ag in Cu3Mo6Se8and of Zn
in “β-Zn4Sb3” is very fast, with tracer diffusion
coefficients on the order of 10-5 to 10-6 cm2/s
in the temperature ranges considered. The temperature dependencies of the
tracer diffusion coefficients denoted above can be described by using
Arrhenius-type relations. The values determined for activation energies are
18.70 + 0.95 kJ/mol for the tracer diffusion of Ag-110m in Cu3Mo6Se8and
11.07 + 0.95 kJ/mol for the tracer diffusion of Zn-65 in “β-Zn4Sb3”.
These values are comparable to the very low activation energy of 9.16 kJ/mol
observed for the diffusion of Ag in the fast ion conductor α-AgI.
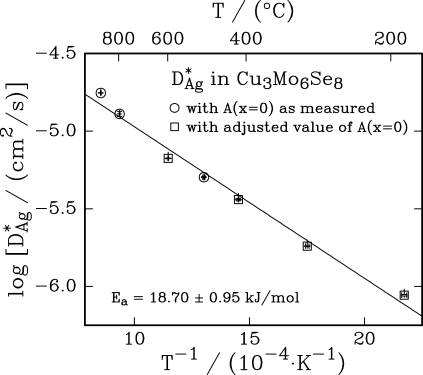
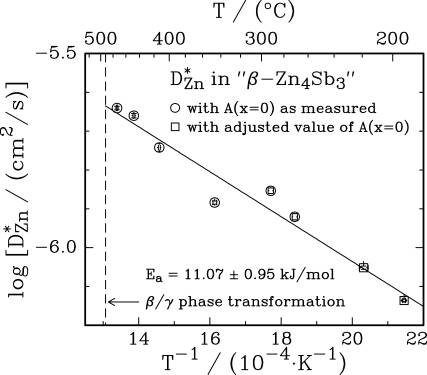
Arrhenius plots of tracer
diffusion coefficients: a) for Ag-110m diffusing in Cu3Mo6Se8
and b) for Zn-65 diffusing in “β-Zn4Sb3”.
Solid State Ionics, 178 (5-6) [2007] 447-456,
article available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2007.01.026